5 Reasons Why Your Torque Wrench Needs to be Calibrated
Whether you’re using a torque wrench in a professional setting or in a home garage, you need to know that your fastener is tightened to a specific...


In today’s heavily regulated environment, an increasing number of companies are required to comply with strict regulatory standards in order to provide goods and services to their customers. The FDA, ISO, OSHA and other governing bodies are becoming increasingly focused on how organizations manage the calibration of their equipment as part of their quality control systems. For instance, the FDA is responsible for the oversight of more than $2.4 trillion in consumption of medical products, food and tobacco (FDA Fact Sheet April 2017). These industries must comply to the Code of Federal Regulations governed by the FDA requiring them to establish and maintain procedures to ensure that equipment is routinely calibrated, inspected, checked, and maintained. These companies are frequently subjected to external audits by their governing bodies to ensure that the various aspects of their calibration program comply to specific standards. Some of the key details auditors will review is evidence that instruments were calibrated at specified intervals and following any change or event that might have affected accuracy or performance. Most organizations allocate the resources needed to complete scheduled calibration, but are often caught off-guard by “unscheduled” calibration requirements. With most company resources already stretched thin, additional personnel is simply not available to properly calibrate instruments as often as needed to ensure compliance with these strict demands.
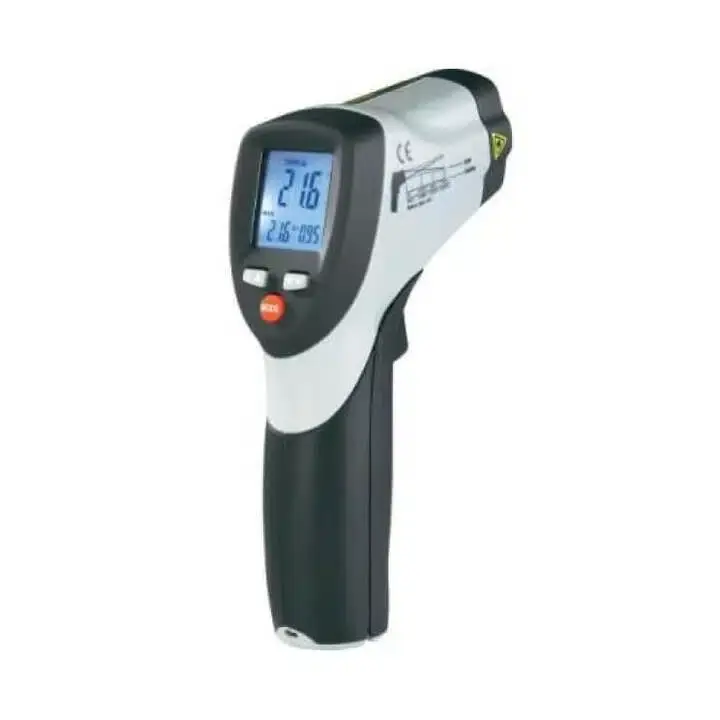
As an example, infrared thermometers are especially prone to needing frequent calibration as they are extremely sensitive to environmental changes which can result from rapidly changing weather conditions. Infrared thermometers are also used for many safety related tasks and are therefore subject to OSHA compliance guidelines. It is critical that these instruments be calibrated whenever the need arises to ensure they are providing accurate readings.
“Even though infrared (IR) thermometers are relatively easy to use, proper calibration can be a very time consuming activity. To ensure the instrument is calibrated correctly, the calibration process should be carried out by trained technicians in a controlled laboratory environment. Various equipment including holding fixtures, black body sources and standard reference thermometers must be used to ensure the accuracy of calibration,” as revealed by Precision Calibration Systems.
It is important to know what factors trigger calibration and re-calibration of your equipment in order to avoid audit non-conformances and maintain the overall integrity of your quality assurance program.



Whether you’re using a torque wrench in a professional setting or in a home garage, you need to know that your fastener is tightened to a specific...
There are many technical factors to be considered when you need to have your Universal Testing Machine calibrated. What size load cell(s) does your...